CAP Health
HBOT, Naturopathy, Massage, Concussion & Whiplash, FSM
Our Peer-Reviewed Research
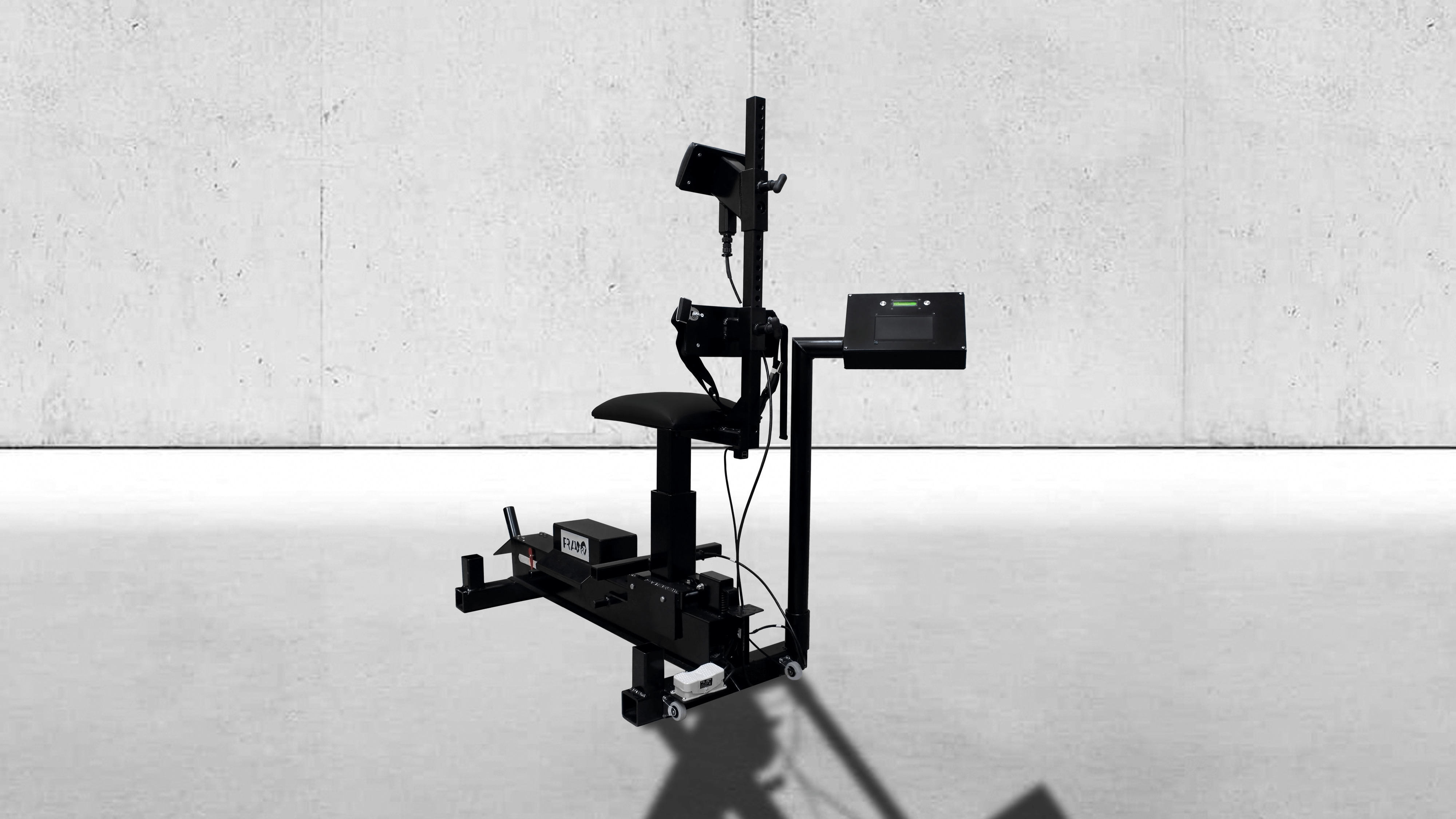
"A Novel Concussion Active Prevention Testing Device for Neck Strength Evaluation During Sub-concussive Impacts"
The paper by Nazarahari, M., Arthur, J. & Rouhani, H. Titled A Novel Testing Device to Assess the Effect of Neck Strength on Risk of Concussion has been published in the Annals of Biomedical Engineering. This journal is historically a prestigious archival journal in biomedical engineering. The U of A article went through 3 rounds of critical peer-review and can be cited as a proof of the validity of the RAM device (in the scope and to the extent discussed in the article).
Specifically the U of A team studied the contribution of individual neck muscles on the reduction of angular head acceleration in simulated sports contact. The goal was to identify the optimal ratio of strength between muscle groups that strength training should strive to achieve which reduces angular acceleration in common scenarios of impact.
“A Novel Concussion Active Prevention Testing Device for Neck Strength Evaluation During Sub-concussive Impacts” paper was presented at The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering (CSME) International Congress 2018 in Toronto, ON, Canada. The RAM technology was clinically validated by the CSME.
Read the press release: Research is Being Conducted with U of A to Test Neck Strength using the CAP RAM
"An Accessible, 16-Week Neck Strength Training Program Improves Head Kinematics Following Chest Perturbation in Young Soccer Athletes"
Auckland University of Technology has published an independent peer-reviewed study analyzing our CAP data from the kinematic response to impulsive loading. By analyzing the relationship between strength performance and the movements of the head we can predict a strategy and protective levels of strength that the athlete can develop to reduce susceptibility to concussions.
Read the abstract at https://doi.org/10.1123/jsr.2020-0537.
Neck Strength & Biomechanics Research
- Barth, J. T., Freeman, J. R., Broshek, D. K., & Varney, R. N. (2001). Acceleration-Deceleration Sport-Related Concussion: The Gravity of It All.Journal of Athletic Training,36(3), 253-256. Website
- Broshek, D. K., Kaushik, T., Freeman, J. R., Erlanger, D., Webbe, F., & Barth, J. T. (2005). Sex differences in outcome following sports-related concussion. Journal of Neurosurgery,102(5), 856-863. DOI
- Caccese, J. B., Buckley, T. A., Tierney, R. T., Arbogast, K. B., Rose, W. C., Glutting, J. J., & Kaminski, T. W. (2017). Head and neck size and neck strength predict linear and rotational acceleration during purposeful soccer heading Sports Biomechanics, 1-15. DOI
- Carey, B. (2016, April 08). Stanford researchers measure concussion forces in detail. Website
- Cohen, M. (2012, September 28). Syracuse tries to decrease risk of concussions by neck-strengthening. Website
- Collins, C. L., Fletcher, E. N., Fields, S. K., Kluchurosky, L., Rohrkemper, M. K., Comstock, R. D., & Cantu, R. C. (2014). Neck Strength: A Protective Factor Reducing Risk for Concussion in High School Sports. The Journal of Primary Prevention,35(5), 309-319. DOI
- Costa-Paz, M., Aponte-Tinao, L., & Muscolo, D. L. (1999). Injuries to polo riders: A prospective evaluation. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 33(5), 329-331. DOI
- Covassin, T., Swanik, C. B., & Sachs, M. L. (2003). Concussions Among United States High School and Collegiate Athletes. Journal of Athletic Training,38(3), 238-244. Website
- Dezman, Z. D., Ledet, E. H., & Kerr, H. A. (2013). Neck Strength Imbalance Correlates With Increased Head Acceleration in Soccer Heading.Sports Health: A Multidisciplinary Approach,5(4), 320-326. DOI
- Dick, R. W. (2009). Is there a gender difference in concussion incidence and outcomes?. British Journal of Sports Medicine,43(Suppl_1), I46-I50. DOI
- Eckner, J. T., Oh, Y. K., Joshi, M. S., Richardson, J. K., & Ashton-Miller, J. A. (2014). Effect of Neck Muscle Strength and Anticipatory Cervical Muscle Activation on the Kinematic Response of the Head to Impulsive Loads. The American Journal of Sports Medicine,42(3), 566-576. DOI
- Field, M., Collins, M. W., Lovell, M. R., & Maroon, J. (2003). Does age play a role in recovery from sports-related concussion? A comparison of high school and collegiate athletes. The Journal of Pediatrics,142(5), 546-553. DOI
- Frommer, L. J., Gurka, K. K., Cross, K. M., Ingersoll, C. D., Comstock, R. D., & Saliba, S. A. (2011). Sex Differences in Concussion Symptoms of High School Athletes. Journal of Athletic Training,46(1), 76-84. DOI
- Gessel, L. M., Fields, S. K., Collins, C. L., Dick, R. W., & Comstock, R. D. (2007). Concussions Among United States High School and Collegiate Athletes. Journal of Athletic Training,42(4), 495-503. Website
- Gregory, S. (2013, February 21). Neck Strength Predicts Concussion Risk, Study Says. Website
- Le Flao, E., Pichardo, A., Ganpatt, S., & Oranchuk, D. (2021). An Accessible, 16-Week Neck Strength Training Program Improves Head Kinematics Following Chest Perturbation in Young Soccer Athletes. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation. 30. 1158-1165. DOI
- Lee, Y., Shin, M. M., & Lee, W. (2015). Effects of shoulder stabilization exercise on pain and function in patients with neck pain. Journal of Physical Therapy Science,27(12), 3619-3622. DOI
- Lincoln, A. E., Caswell, S. V., Almquist, J. L., Dunn, R. E., Norris, J. B., & Hinton, R. Y. (2011). Trends in Concussion Incidence in High School Sports. The American Journal of Sports Medicine,39(5), 958-963. DOI
- Lott, J. R. (2017, August 31). Concussions occur in soccer and other sports, too — but yeah, let’s go after all-American football. Website
- Meaney, D. F., & Smith, D. H. (2011). Biomechanics of Concussion.Clinics in Sports Medicine,30(1), 19-31. DOI
- Schneider, K. J., Meeuwisse, W. H., Nettel-Aguirre, A., Barlow, K., Boyd, L., Kang, J., & Emery, C. A. (2014). Cervicovestibular rehabilitation in sport-related concussion: a randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Sports Medicine,48(17), 1294-1298. DOI
- Tierney, R. T., Sitler, M. R., Swanik, C. B., Swanik, K. A., Higgins, M., & Torg, J. (2005). Gender Differences in Head Neck Segment Dynamic Stabilization during Head Acceleration. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise,37(2), 272-279. DOI
- Viano, D. C., Casson, I. R., & Pellman, E. J. (2007). Concussion in Professional Football: Biomechanics of the StruckPlayer—Part 14. Neurosurgery,61(2), 313-328. DOI
- Vidal, P. G., Goodman, A. M., Colin, A., Leddy, J. J., & Grady, M. F. (2012). Rehabilitation Strategies for Prolonged Recovery in Pediatric and Adolescent Concussion. Pediatric Annals,41(9), 1-7. DOI
- Yang, X., & Cheng, B. (2010). Neuroprotective and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Ketogenic Diet on MPTP-induced Neurotoxicity. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience,42(2), 145-153. DOI
Concussion Assessment
- Favorov, O. V., Francisco, E., Holden, J., Kursun, O., Zai, L., & Tommerdahl, M. (2019). Quantification of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury via Cortical Metrics: Analytical Methods. Military Medicine, 184(Supplement_1), 228-236. doi:10.1093/milmed/usy411. Full text, Poster.
- Francisco, E., Holden, J.,Tommerdahl, M. (2017). Assessing traumatic brain injury via cortical metrics. Poster.
- Francisco, E. M., Holden, J. K., Nguyen, R. H., Favorov, O. V., & Tommerdahl, M. (2015). Percept of the duration of a vibrotactile stimulus is altered by changing its amplitude. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 9. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2015.00077. Full text.
- King DA, Hume PA, Tommerdahl M (2016) Use of the Brain-Gauge Somatosensory Assessment for Monitoring Recovery from Concussion: A Case Study. Journal of Physiotherapy Research. Vol.2 No.1:3. Full text.
- Pearce, A. J., Tommerdahl, M., & King, D. A. (2019). Neurophysiological abnormalities in individuals with persistent post-concussion symptoms. Neuroscience, 408, 272-281. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.04.019. Full text.
- Pearce, Alan & King, Doug & Cummins, Cloe & Tommerdahl, Mark. (2018). Understanding the neurophysiological component of persistent fatigue following concussion using transcranial magnetic stimulation and neurosensory assessment (Poster). Full text.
- Powell, Dylan. (2018). Exploratory Analysis of the effects of University Rugby on Brain Healthmonitoredvia a Somatosensory Device. Full text.
- Tommerdahl, M., Dennis, R. G., Francisco, E. M., Holden, J. K., Nguyen, R., & Favorov, O. V. (2016). Neurosensory Assessments of Concussion. Military Medicine, 181(5S), 45-50. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-15-00172. Full text, Poster.
Rehabilitation
- Gasior, M., Rogawski, M. A., & Hartman, A. L. (2006). Neuroprotective and disease-modifying effects of the ketogenic diet. Behavioural Pharmacology, 17(5-6), 431-439. DOI
- Jamall, O. A., Feeney, C., Zaw-Linn, J., Malik, A., Niemi, M. E.K., Tenorio-Jimenez, C., Ham, T. E., Jilka, S. R., Jenkins, P. O., Scott, G., Li, L. M., Gorgoraptis, N., Baxter, D., Sharp, D. J. and Goldstone, A. P. (2016), Prevalence and correlates of vitamin D deficiency in adults after traumatic brain injury. Clinical Endocrinology, 85, 636–644. DOI
- Shohami, E., Beit-Yannai, E., Horowitz, M., & Kohen, R. (1997). Oxidative Stress in Closed-Head Injury: Brain Antioxidant Capacity as an Indicator of Functional Outcome. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 17(10), 1007-1019. DOI
- Stvolinsky, S. L., Kukley, M. L., Dobrota, D., Matejovicova (Vachova), M., Tkac, I., & Boldyrev, A. A. (february 1999). Carnosine: An Endogenous Neuroprotector in the Ischemic Brain. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 19(1), 45-56. DOI
- Sussman, E. S., Ho, A. L., Pendharkar, A. V., & Ghajar, J. (2016). Clinical evaluation of concussion: the evolving role of oculomotor assessments. Neurosurgical Focus, 40(4). DOI
Neuro Health
- Chiu, J., Tommerdahl, M., Whitsel, B. & Favorov, O. Stimulus-dependent spatial patterns of response in SI cortex. BMC Neuroscience 6, 47 (2005). DOI
- Clark, M. D., Varangis, E. M., Champagne, A. A., Giovanello, K. S., Shi, F., Kerr, Z. Y., … Guskiewicz, K. M. (2018). Effects of Career Duration, Concussion History, and Playing Position on White Matter Microstructure and Functional Neural Recruitment in Former College and Professional Football Athletes. Radiology, 286(3), 967-977. DOI
- Favorov, O., Awan, O. & Tommerdahl, M. Minicolumnar Model of Somatosensory Perceptual Abnormalities in Autism. Society for Neuroscience 346.5, (2008).
- Favorov, O., Hester, J., Kelly, D., Ryder, D. & Tommerdahl, M. in Computational Models for Neuroscience (eds. Hecht-Nielsen, R. & McKenna, T.) 25–64 (Springer London, 2003).
- Favorov, O., Hester, J., Kelly, D., Tommerdahl, M. & Whitsel, B. Lateral interactions in cortical networks. Somatosensory processing: from single neuron to brain imaging 187 (2001).
- Favorov, O., Hester, J., Lao, R. & Tommerdahl, M. Spurious dynamics in somatosensory cortex. Behavioural Brain Research 135, 75–82 (2002).
- Favorov, O. & Kursun, O. Neocortical Layer 4 is a Pluipotent Function Linearizer. in Society for Neuroscience 261.21, (2009).
- Favorov, O., Whitsel, B., Chiu, J. & Tommerdahl, M. Activation of cat SII cortex by flutter stimulation of contralateral vs. ipsilateral forepaws. Brain Research 1071, 81–90 (2006). DOI
- Folger, S., Tannan, V., Zhang, Z., Holden, J. & Tommerdahl, M. Effects of the N-methyl-D-Aspartate receptor antagonist dextromethorphan on vibrotactile adaptation. BMC neuroscience 9, 87 (2008). DOI
- Francisco, E., Favorov, O. & Tommerdahl, M. in Recent Advances in Autism Spectrum Disorders – Volume II (ed. Fitzgerald, M.) (InTech, 2013).
- Francisco, E., Holden, J., Favorov, O. & Tommerdahl, M. A Method for Dynamically Tracking Differences Between Two Vibrotactile Stimuli. in Society for Neuroscience 178.9, (2008).
- Francisco, E., Holden, J., Nguyen, R., Favorov, O. & Tommerdahl, M. Neurosensory Assessments of Concussion. in Society for Neuroscience 269.02, (2012).
- Francisco, E., Holden, J., Zhang, Z., Baranek, G. & Tommerdahl, M. Sensory Information Processing in Autism. in Society for Neuroscience 635.21, (2009).
- Francisco, E., Holden, J., Zhang, Z., Favorov, O. & Tommerdahl, M. Rate dependency of vibrotactile stimulus modulation. Brain Research 1415, 76–83 (2011).
- Francisco, E., Tannan, V., Zhang, Z., Holden, J. & Tommerdahl, M. Vibrotactile amplitude discrimination capacity parallels magnitude changes in somatosensory cortex and follows Weber’s Law. Experimental brain research 191, 49–56 (2008).
- Holden, J., Francisco, E., Zhang, Z., Baric, C. & Tommerdahl, M. An Undergraduate Laboratory Exercise to Study Weber’s Law. Journal of undergraduate neuroscience education: JUNE: a publication of FUN, Faculty for Undergraduate Neuroscience 9, A71–74 (2011).
- Holden, J. et al. A novel device for the study of somatosensory information processing. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 204, 215–220 (2012).
- Hollins, M., Goble, A., Whitsel, B. & Tommerdahl, M. Time Course and Action Spectrum of Vibrotactile Adaptation. Somatosensory & Motor Research 7, 205–221 (1990).
- Juliano, S. L., Code, R. A., Tommerdahl, M. & Eslin, D. E. Development of metabolic activity patterns in the somatosensory cortex of cats. Journal of Neurophysiology 70, 2117–2127 (1993).
- Juliano, S. L., Whitsel, B., Tommerdahl, M. & Cheema, S. S. Determinants of patchy metabolic labeling in the somatosensory cortex of cats: a possible role for intrinsic inhibitory circuitry. The Journal of Neuroscience 9, 1–12 (1989).
- Khan, S. et al. Neurophysiological Correlates of Tactile Sensitivities in ASD. in IMFAR (2013).
- Kohn, A., Metz, C., Quibrera, M., Tommerdahl, M. & Whitsel, B. Functional neocortical microcircuitry demonstrated with intrinsic signal optical imaging in vitro. Neuroscience 95, 51–62 (1999).
- Kohn, A., Metz, C., Tommerdahl, M. & Whitsel, B. Stimulus-Evoked Modulation of Sensorimotor Pyramidal Neuron EPSPs. Journal of Neurophysiology 88, 3331–3347 (2002).
- Kohn, A., Pinheiro, A., Tommerdahl, M. & Whitsel, B. Optical imaging in vitro provides evidence for the minicolumnar nature of cortical response: NeuroReport 8, 3513–3517 (1997).
- Kursun, O., Tommerdahl, M. & Favorov, O. Analysis of Effects of Parkinson’s Disease on the Somatosensory System via CM-4 Tactile Stimulator. in International Conference on Applied Informatics and Health and Life Sciences (2013).
- Lee, C.-J., Whitsel, B. & Tommerdahl, M. Mechanisms Underlying Somatosensory Cortical Dynamics: II. In vitro Studies. Cerebral Cortex 2, 107–133 (1992).
- Lee, J., Favorov, O., Tommerdahl, M., Lee, J. & Whitsel, B. Attenuated Glial K(+) Clearance Contributes to Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation Via Depolarizing GABA in Dorsal Horn Neurons of Rat Spinal Cord. Experimental Neurobiology 23, 53–64 (2014).
- Lee, J., Favorov, O., Tommerdahl, M. & Whitsel, B. Mechanism of Sodium Fluoride-Induced Volume Reduction in Rat Hippocampal Slices. in Society for Neuroscience 736.15, (2008).
- Lee, J., Favorov, O., Tommerdahl, M. & Whitsel, B. Activity-Dependent GABA Excitation of Sensorimotor Cortical Pyramidal Neurons. in Society for Neuroscience 78.18, (2009).
- Lee, J., Tommerdahl, M., Favorov, O. & Whitsel, B. Optically Recorded Response of the Superficial Dorsal Horn: Dissociation From Neuronal Activity, Sensitivity to Formalin-Evoked Skin Nociceptor Activation. Journal of Neurophysiology 94, 852–864 (2005).
- Lee, J. et al. Columnar distribution of activity dependent gabaergic depolarization in sensorimotor cortical neurons. Molecular Brain 5, 33 (2012).
- Lee, K. et al. The influence of continuous theta-burst stimulation over the primary somatosensory cortex on temporal order judgment perception. in Society for Neuroscience 377.12, (2012).
- Lee, K. et al. Continuous theta-burst stimulation modulates tactile synchronization. BMC neuroscience 14, 89 (2013).
- Maeda, Y. et al. Functional deficits in carpal tunnel syndrome reflect reorganization of primary somatosensory cortex. Brain: A Journal of Neurology 137, 1741–1752 (2014).
- Nebel, M. B. et al. Temporomandibular disorder modifies cortical response to tactile stimulation. The Journal of Pain: Official Journal of the American Pain Society 11, 1083–1094 (2010).
- Nelson, A. et al. Dopamine alters tactile perception in Parkinson’s disease. The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. Le Journal Canadien Des Sciences Neurologiques 39, 52–57 (2012).
- Nguyen, R. et al. Neurosensory assessments of migraine. Brain Research 1498, 50–58 (2013).
- Nguyen, R. et al. Vibrotactile discriminative capacity is impacted in a digit-specific manner with concurrent unattended hand stimulation. Experimental Brain Research (2014). DOI
- Nguyen, R. et al. Centrally-mediated sensory information processing is impacted with increased alcohol consumption in college-aged individuals. Brain Research 1492, 53–62 (2013).
- Nguyen, R. et al. Neurosensory assessments of migraine. in Society for Neuroscience 269.13, (2012).
- Nguyen, R. et al. An undergraduate laboratory exercise to study sensory inhibition. Journal of undergraduate neuroscience education: JUNE: a publication of FUN, Faculty for Undergraduate Neuroscience 11, A169–173 (2013).
- Puts, N., Edden, R., Wodka, E., Mostofsky, S. & Tommerdahl, M. A vibrotactile behavioral battery for investigating somatosensory processing in children and adults. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 218, 39–47 (2013).
- Puts, N. et al. A Combined GABA-MRS and Behavioral Study in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. in International Meeting for Autism Research (2013).
- Puts, N., Wodka, E., Tommerdahl, M., Mostofsky, S. & Edden, R. Impaired tactile processing in children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Neurophysiology 111, 1803–1811 (2014).
- Rai, N., Premji, A., Tommerdahl, M. & Nelson, A. Continuous theta-burst rTMS over primary somatosensory cortex modulates tactile perception on the hand. Clinical Neurophysiology: Official Journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology 123, 1226–1233 (2012).
- Shin, H., & Moore, C. I. (2019). Persistent Gamma Spiking in SI Nonsensory Fast Spiking Cells Predicts Perceptual Success. Neuron. DOI
- Simons, S., Chiu, J., Favorov, O., Whitsel, B. & Tommerdahl, M. Duration-Dependent Response of SI to Vibrotactile Stimulation in Squirrel Monkey. Journal of Neurophysiology 97, 2121–2129 (2007).
- Simons, S. et al. Amplitude-dependency of response of SI cortex to flutter stimulation. BMC Neuroscience 6, 43 (2005).
- Tannan, V., Dennis, R. & Tommerdahl, M. A novel device for delivering two-site vibrotactile stimuli to the skin. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 147, 75–81 (2005).
- Tannan, V., Dennis, R. & Tommerdahl, M. Stimulus-dependent effects on tactile spatial acuity. Behavioral and Brain Functions 1, 1–11 (2005).
- Tannan, V., Dennis, R., Zhang, Z. & Tommerdahl, M. A portable tactile sensory diagnostic device. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 164, 131–138 (2007).
- Tannan, V., Holden, J., Zhang, Z., Baranek, G. & Tommerdahl, M. Perceptual metrics of individuals with autism provide evidence for disinhibition. Autism Research 1, 223–230 (2008).
- Tannan, V., Simons, S., Dennis, R. & Tommerdahl, M. Effects of adaptation on the capacity to differentiate simultaneously delivered dual-site vibrotactile stimuli. Brain Research 1186, 164–170 (2007).
- Tannan, V., Whitsel, B. & Tommerdahl, M. Vibrotactile adaptation enhances spatial localization. Brain Research 1102, 109–116 (2006).
- Tavassoli, T. et al. Tactile Reactivity in Autism Spectrum Disorders. in International Meeting for Autism Research (2013).
- Thieme, K. et al. Pain inhibition in Fibromyalgia. The Journal of Pain 12, P73 (2011).
- Tommerdahl, M., Chiu, J., Whitsel, B. & Favorov, O. Minicolumnar patterns in the global cortical response to sensory stimulation. Neocortical Modularity and the Cell Minicolumn 145–160 (2005).
- Tommerdahl, M. et al. Response of Anterior Parietal Cortex to Different Modes of Same-Site Skin Stimulation. Journal of Neurophysiology 80, 3272–3283 (1998).
- Tommerdahl, M., Delemos, K. A., Vierck, C., Favorov, O. & Whitsel, B. Anterior parietal cortical response to tactile and skin-heating stimuli applied to the same skin site. Journal of Neurophysiology 75, 2662–2670 (1996).
- Tommerdahl, M., Delemos, K. A., Whitsel, B., Favorov, O. & Metz, C. Response of Anterior Parietal Cortex to Cutaneous Flutter Versus Vibration. Journal of Neurophysiology 82, 16–33 (1999).
- Tommerdahl, M. et al. Neurosensory Assessments Of Concussion. in MHSRS-ATACC MHSRS-12-184, (2012).
- Tommerdahl, M., Favorov, O., Whitsel, B., Nakhle, B. & Gonchar, Y. A. Minicolumnar Activation Patterns in Cat and Monkey SI Cortex. Cerebral Cortex 3, 399–411 (1993).
- Tommerdahl, M., Favorov, O. & Whitsel, B. Optical imaging of intrinsic signals in somatosensory cortex. Behavioural Brain Research 135, 83–91 (2002).
- Tommerdahl, M., Favorov, O. & Whitsel, B. Effects of high-frequency skin stimulation on SI cortex: mechanisms and functional implications. Somatosensory & Motor Research 22, 151–169 (2005).
- Tommerdahl, M., Favorov, O. & Whitsel, B. Dynamic representations of the somatosensory cortex. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 34, 160–170 (2010).
- Tommerdahl, M. et al. Human vibrotactile frequency discriminative capacity after adaptation to 25 Hz or 200 Hz stimulation. Brain Research 1057, 1–9 (2005).
- Tommerdahl, M., R, B., Whitsel, B. & S, J. A method for reconstructing patterns of somatosensory cerebral cortical activity. ISA transactions 25, 71–76 (1985).
- Tommerdahl, M., Simons, S., Chiu, J., Favorov, O. & Whitsel, B. Response of SI cortex to ipsilateral, contralateral and bilateral flutter stimulation in the cat. BMC Neuroscience 6, 29 (2005).
- Tommerdahl, M., Simons, S., Chiu, J., Favorov, O. & Whitsel, B. Ipsilateral Input Modifies the Primary Somatosensory Cortex Response to Contralateral Skin Flutter. The Journal of Neuroscience 26, 5970–5977 (2006).
- Tommerdahl, M., Tannan, V., Cascio, C., Baranek, G. & Whitsel, B. Vibrotactile adaptation fails to enhance spatial localization in adults with autism. Brain Research 1154, 116–123 (2007).
- Tommerdahl, M., Tannan, V., Holden, J. & Baranek, G. Absence of stimulus-driven synchronization effects on sensory perception in autism: Evidence for local underconnectivity? Behavioral and brain functions: BBF 4, 19 (2008).
- Tommerdahl, M., Tannan, V., Zachek, M., Holden, J. & Favorov, O. Effects of stimulus-driven synchronization on sensory perception. Behavioral and brain functions: BBF 3, 61 (2007).
- Tommerdahl, M., Whitsel, B., Favorov, O., Metz, C. & O’Quinn, B. L. Responses of Contralateral SI and SII in Cat to Same-Site Cutaneous Flutter Versus Vibration. Journal of Neurophysiology 82, 1982–1992 (1999).
- Tommerdahl, M. et al. Effects of Spinal Dorsal Column Transection on the Response of Monkey Anterior Parietal Cortex to Repetitive Skin Stimulation. Cerebral Cortex 6, 131–155 (1996).
- Tommerdahl, M. & Whitsel, B. in Somesthesis and the Neurobiology of the Somatosensory Cortex (eds. Franzén, P. O., Johansson, P. R. & Terenius, P. L.) 369–384 (Birkhäuser Basel, 1996).
- Vierck, C., Whitsel, B., Favorov, O., Brown, A. & Tommerdahl, M. Role of primary somatosensory cortex in the coding of pain. Pain 154, 334–344 (2013).
- Wellman, A. D., Coad, S. C., Goulet, G. C., & Mclellan, C. P. (2016). Quantification of Competitive Game Demands of NCAA Division I College Football Players Using Global Positioning Systems. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 30(1), 11-19. DOI
- Whitsel, B. et al. SI Neuron Response Variability Is Stimulus Tuned and NMDA Receptor Dependent. Journal of Neurophysiology 81, 2988–3006 (1999).
- Whitsel, B. et al. Nociceptive afferent activity alters the SI RA neuron response to mechanical skin stimulation. Cerebral Cortex (New York, N.Y.: 1991) 20, 2900–2915 (2010).
- Whitsel, B., Favorov, O., Li, Y., Lee, J. & Tommerdahl, M. Nociceptor Afferent Drive Alters SI Neuron Response to Mechanical Stimulation of the RF. in Society for Neuroscience 562.11, (2009).
- Whitsel, B., Favorov, O., Li, Y., Quibrera, M. & Tommerdahl, M. Area 3a neuron response to skin nociceptor afferent drive. Cerebral Cortex (New York, N.Y.: 1991) 19, 349–366 (2009).
- Whitsel, B. et al. Time-dependence of SI RA neuron response to cutaneous flutter stimulation. Somatosensory & Motor Research 20, 45–69 (2003).
- Whitsel, B., Kelly, E., Xu, M., Tommerdahl, M. & Quibrera, M. Frequency-dependent response of SI RA-class neurons to vibrotactile stimulation of the receptive field. Somatosensory & Motor Research 18, 263–285 (2001).
- Zhang, Z., Francisco, E., Holden, J., Dennis, R. & Tommerdahl, M. The impact of non-noxious heat on tactile information processing. Brain Research 1302, 97–105 (2009).
- Zhang, Z., Francisco, E., Holden, J., Dennis, R. & Tommerdahl, M. Somatosensory Information Processing in the Aging Population. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 3, (2011).
- Zhang, Z., Francisco, E., Holden, J. & Tommerdahl, M. The Impact of Non-noxious Heat on Tactile Information Processing Capacity. in Society for Neuroscience 78.18, (2009).
- Zhang, Z., Holden, J., Baranek, G. & Tommerdahl, M. Sensory Information Processing in Autism. in Society for Neuroscience 178.9, (2008).
- Zhang, Z., Tannan, V., Holden, J., Dennis, R. & Tommerdahl, M. A quantitative method for determining spatial discriminative capacity. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 7, 1–8 (2008).
- Zhang, Z. et al. Altered central sensitization in subgroups of women with vulvodynia. The Clinical journal of pain 27, 755–763 (2011).
You may also be interested in the following services: